nasa tools measure thick icecaps|sea ice thickness : specialty store With high-resolution data from ICESat-2’s laser altimeter, scientists will track changes to Earth’s polar ice caps – regions that are a harbinger of warming temperatures . 11 de set. de 2021 · A photo of her legs dangling over the roof of her house, pictures of self-inflicted cuts on her body and a final post of train tracks with the words ‘good bye,’ made the morning she died, all bore resemblance to the other reported accounts of .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBUpdated. Jan 19, 2024. Project ID. LowOnFire 1.18. Description. Comments (21) Files. Images. Relations. Description. Low fire on your screen! For versions 1.20 down to 1.8! .
Measuring ice depths across Earth is important for understanding aquatic and cryospheric processes, learning how ice relates to regulating the climate and sea level, determining safe transportation routes, tracking the ways ice thickness influences animal behavior patterns, and .
Clouds, aerosols, even the bumps and dips on the ice itself can play a role. To .
sea ice thickness
nasa icesat 2
Clouds, aerosols, even the bumps and dips on the ice itself can play a role. To explore how these factors interact and impact sea ice melting, NASA is flying two aircraft . NASA helps find thawing permafrost adds to near-term global warming. by Sally Younger. Pasadena CA (SPX) Oct 30, 2024. A new study, co-authored by NASA scientists, . With high-resolution data from ICESat-2’s laser altimeter, scientists will track changes to Earth’s polar ice caps – regions that are a harbinger of warming temperatures . The first months of ICESat-2 data collected over Arctic and Antarctic sea ice reveal thin ice, thick ice, and features such as ice ridges. Areas of open water in the cracks between the ice floes, called leads, stand out in .
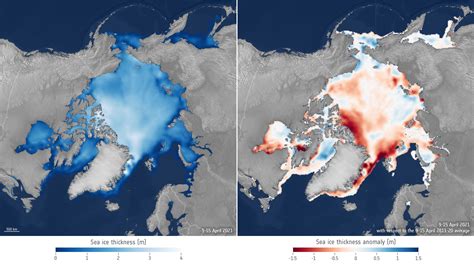
ARCSIX Analyzes Arctic Sea Ice Loss. June 15, 2024 JPEG. The layer of sea ice that caps the Arctic Ocean hits its maximum thickness during the long, dark polar night that . The new study was undertaken as part of the Global Carbon Project’s RECCAP-2 effort, which brings together different science teams, tools, and datasets to assess regional . New research out of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California shows that in the central Arctic, away from the coasts, fall sea ice now hovers around 4.2 feet . A closeup view of one track is revealed, showing how the ICESat-2 laser can measure ice freeboard (height above sea level), which can be used to calculate total ice thickness. The visualization concludes by showing monthly .
Computer models are critical tools for understanding the future of a changing planet, including melting ice andrising seas. A new NASA sea level simulator lets you bury Alaska’s Columbia glacier in snow, and, year by year, .Data from NASA's GRACE and GRACE Follow-On satellites show that the land ice sheets in both Antarctica (upper chart) and Greenland (lower chart) have been losing mass since 2002. The GRACE mission ended in June 2017. The GRACE Follow-On mission began collecting data in June 2018 and is continuing to monitor both ice sheets. Scientists have used NASA's ICESat-2 to measure the thickness of Arctic sea ice, as well as the depth of snow on the ice. Here, ridges and cracks have formed in sea ice in the Arctic Ocean. . “The extraordinary accuracy .
In some areas, these layers result in ice sheets that are several miles (several kilometers) thick. Researchers drill ice cores from deep (sometimes more than a mile [1.6 kilometers]) inside the polar ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica, as well as some high-latitude ice caps and mountain glaciers. In some areas, these layers result in ice sheets that are several miles (several kilometers) thick. Researchers drill ice cores from deep (sometimes more than a mile [1.6 kilometers]) inside the polar ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica, as well as some high-latitude ice caps and mountain glaciers.The ICESat mission will provide multi-year elevation data needed to determine ice sheet mass balance as well as cloud property information, especially for stratospheric clouds common over polar areas. It will also provide topography and vegetation data around the globe, in addition to the polar-specific coverage over the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets.
Since the late 1970's, NASA has been monitoring changes in the Greenland Ice Sheet. Recent analysis of seven years of surface elevation readings from NASA's ICESat satellite and four years of laser and and ice-penetrating radar data from NASA's airborne mission Operation IceBridge shows us how the surface elevation of the ice sheet has changed.The . A Technological Leap. ICESat-2 represents a major technological leap in our ability to measure changes in ice height. Its Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS) measures height by timing how long it takes individual light photons to travel from the spacecraft to Earth and back. Because snowfall puts an additional layer of snow over sea ice, even some of NASA’s most powerful altimeter systems in space struggle to measure the thickness of the ice. Data from drones flying at low altitudes can help scientists measure this changing thickness more accurately as Arctic sea ice waxes and wanes with the seasons.The instrument to measure the surface temperature of Jupiter’s moon Europa has arrived at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Europa Clipper's Thermal Imager Delivered to JPL How will Europa Clipper see through Europa's thick ice shell to study the moon's ocean?
nasa ice melting
ICESat-2 (short for Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite), slated to launch in 2018, will use lasers and a very precise detection instrument to measure the elevation of Earth’s surface. By timing how long it takes laser beams to travel from the satellite to Earth and back, scientists can calculate the height of glaciers, sea ice, forests, lakes and more – including the changing ice . Nearby, a specially built drill bored into the thick ice sheet twenty-four hours a day under the perpetual Arctic sun. Essentially a sharpened pipe rotating on a long, loose cable, the drill pulled up cores of ice from which Alley and others would glean climate information. Paleoclimatology; Introduction; Written in the Earth; A Record from the . The Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 will measure the height of Earth from space, creating a record of the planet’s elevation in unprecedented detail and precision. With high-resolution data from ICESat-2’s laser altimeter, scientists will track changes to Earth’s polar ice caps – regions that are a harbinger of warming temperatures worldwide. The mission will .First, warmer temperatures at lower elevations along the ice sheet’s edges melt ice, and the resulting meltwater flows into the ocean. Secondly, if the ice sheet is large enough, ice can extend to the coasts and flow into the ocean, where it breaks and floats away as icebergs.In some cases, ice will remain intact as it flows into the ocean, staying connected to the ice sheet and creating .
Credit: NASA Arctic Credit: NASA Antarctic Land ice, such as the ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica or glaciers in the Himalaya, builds up from centuries’ worth of snowfall. It can be miles thick. The Antarctic ice sheet has a mean thickness of 1.6 miles (2.2 km), for example, and reaches a maximum of almost 3 miles (4.8 km) thick. In the 21st century, two new sensing systems have proven to be invaluable complements to the satellite altimetry record. In 2002, NASA and the German space agency launched the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) twin satellites. These measure the movement of mass, and hence gravity, around Earth every 30 days.
In September, NASA will launch ICESat-2, which uses a laser instrument to precisely measure the changing elevation of ice around the world, allowing scientists to see whether ice sheets and glaciers are accumulating .
Editor’s Note—This article is one in a series about how NASA and other science institutions measure and monitor sea level rise. Find the other stories here.. Earth’s ice sheets and glaciers store a vast amount of water on land—as much as 69 percent of the planet’s fresh water, according to the U.S. National Snow & Ice Data Center.Current news and data streams about global warming and climate change from NASA. Credits. Ice, which covers 10 percent of Earth's surface, is disappearing rapidly. Select a topic below to see how climate change has affected glaciers, sea ice, and continental ice sheets worldwide. Vital Signs of the Planet: Global Climate Change and Global . Now, a new NASA visualization of the age of Arctic sea ice shows how sea ice has been growing and shrinking, spinning, melting in place and drifting out of the Arctic for the past three decades. . a measure of the microwave energy emitted by sea ice that is influenced by the ice’s temperature, salinity, surface texture and the layer of snow . In the 21st century, two new sensing systems have proven to be invaluable complements to the satellite altimetry record. In 2002, NASA and the German space agency launched the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) twin satellites. These measure the movement of mass, and hence gravity, around Earth every 30 days.

When NASA ’s Galileo spacecraft sent back images and data of the Jovian moon Europa, scientists began thinking seriously that life just might exist on this enigmatic, frozen world.. Europa appears to have all the conditions necessary for the emergence of life: liquid water, organic chemicals, and energy. A layer of ice covers Europa, but there is strong evidence – . An Airborne Mission for Earth’s Polar Ice. NASA’s Operation IceBridge images Earth’s polar ice in unprecedented detail to better understand processes that connect the polar regions with the global climate system. IceBridge utilizes a highly specialized fleet of research aircraft and the most sophisticated suite of innovative science instruments ever assembled to .By measuring the time between the outgoing and returning signal, . (ICESat-2, for instance, has a footprint with a 14-meter diameter.) Lasers cannot penetrate thick clouds, and their signals reflect off the top of the snow layer. . The Sea Level Change Data Pathfinder on NASA’s Earthdata site highlights tools used by researchers to study .
Atmospheric Scientist - Atmospheric scientists study the weather and climate and examine how those conditions affect human activity and the earth in general. Most atmospheric scientists work indoors in weather stations, offices, or laboratories. Occasionally, they do fieldwork, which means working outdoors to examine the weather.
icesat 2 depth
ICESat-2 represents a major technological leap in our ability to measure changes in ice height. Its Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS) measures height by timing how long it takes individual light photons to travel from the spacecraft to Earth and back. The mass of the Antarctic ice sheet has changed over the last decades. Research based on observations from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellites (2002-2017) and GRACE Follow-On (since 2018 - ) indicates that between 2002 and 2023, Antarctica shed approximately 150 gigatons of ice per year, causing global sea level to rise by .

ice thickness nasa
ice cover in the arctic
arctic sea ice measurements
Resultado da Com símbolos distribuídos em cinco colunas e 15 linhas diferentes, este jogo de cassino virtual permite que suas recompensas cheguem a cinco vezes o valor apostado. .
nasa tools measure thick icecaps|sea ice thickness